Schedule a Call Back
Why SMEs should start work on E-Invoices?
 Interviews
Interviews- Jul 01,19
- Interoperability, or any-to-any formatting. Hundreds of softwares are used by companies large and small. It should be possible for everyone to participate and transact with each other. There should be easily available export and import tools to facilitate easy data movements.
- Cost: The cost of converting data from their existing systems to the formats desired by the regulator should be minimum or nil. If there is a large one-time cost to upgrade systems to be ready for e-Invoices, it is a strong deterrent, especially for SMEs
- Tamper Proof: The invoices should be completely tamper proof, both authenticity and integrity should be maintained for a reasonable amount of time which supports audit. Equal Treatment or Catch All method made it clear that paper and electronic were treated equally.
Related Stories
IRIS and Logo Infosoft’s Vyapari- a free and GST-compliant ERP software for MSMEs
A GST Suvidha Provider (GSP) appointed by GSTN and a structured data solutions company, IRIS Business Services and Logo Infosoft, an established IT solution company has introduced a free version of ..
Read moreWhy SMEs should start work on E-Invoices?
Vinod Subramanian delves into the framework of e-Invoices and sheds light over adoption of similar reforms globally. Here are his few observations:
Read moreIRIS and Logo Infosoft’s Vyapari- a free and GST-compliant ERP software for MSMEs
Vyapari is validated through stringent evaluation criteria for quality and ease of use. Being simple and easy to use, Vyapari automates the complete accounting and compliance process of MSMEs from b..
Read moreRelated Products
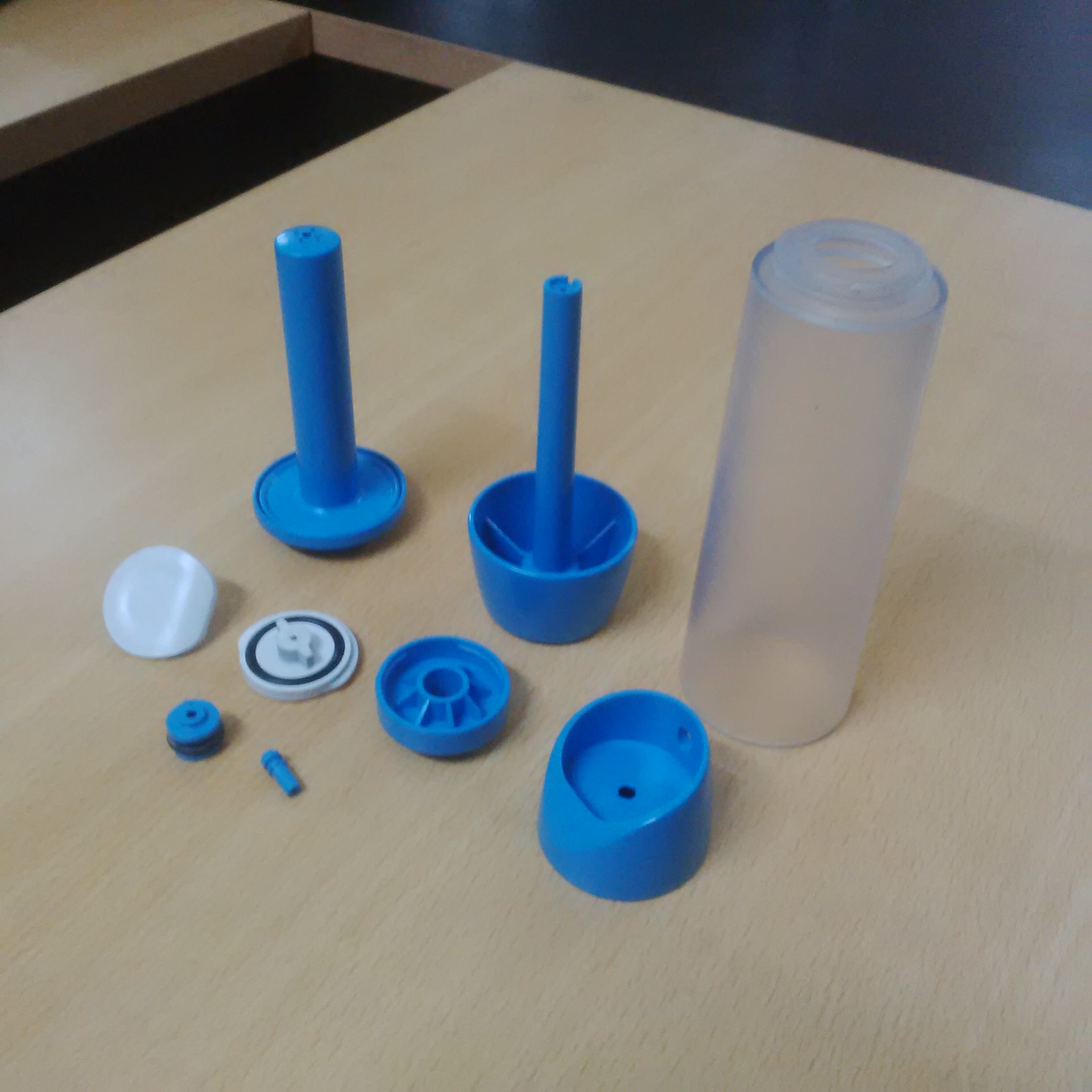

Product Design, Engineering, and Prototyping
"CGCE P Ltd", provides the latest design in rapid prototyping services. Using the latest technology, 3D Printing, FDM, SLA, Vacuum Casting and CNC Machining, CGCE can provide the best prototype soluti Read more

Power Mill
* Create precision complex parts with advanced CNC programming Read more