Schedule a Call Back
Digitisation strengthens our quality management: Anand Mishra
 Articles
Articles- Nov 29,25

Related Stories

Digitisation strengthens our quality management: Anand Mishra
In this interview, Anand Mishra, Vice President – QMS & ESG, Ghodawat Consumer Ltd, discusses how integrated quality systems and sustainability-driven innovation are strengthening GCL’s FMCG lea..
Read more
Can AI be the game changer for Indian manufacturers?
While manpower issues and quality are driving adoption of industrial automation, cost and lack of knowledge are causing hindrances. Artificial intelligence (AI) can be the game changer, writes Rakes..
Read more
Ace Designers is targeting $1 billion by 2029: T K Ramesh
In this exclusive interview with Rakesh Rao, T K Ramesh, MD, Ace Designers Ltd, speaks about opportunities in India’s manufacturing sector, challenges facing the machine tool industry, and the com..
Read moreRelated Products
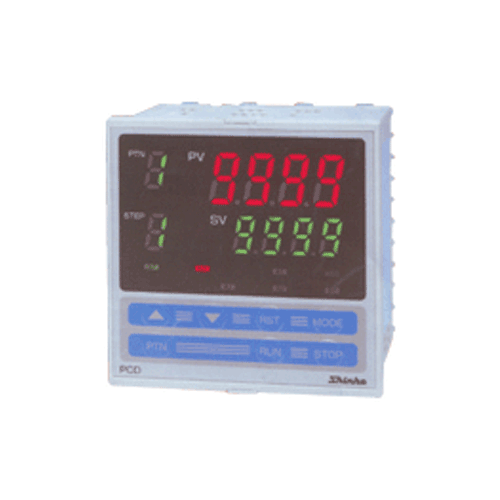

Programmable Controllers - Pcd-33a Series
Pro-Med Instruments (P) Ltd offers a wide range of programmable controllers - PCD-33A Series.
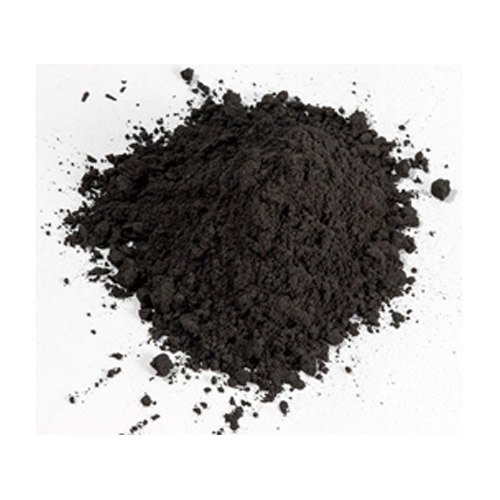

Gasket Graphite Powder
Arihant Packing & Gasket Company offers a wide range of gasket graphite powder.
Asahi Kasei expands 3D printing filament sales in North America
Asahi Kasei, a leading resin and compounding technology provider, has initiated the sales of 3D printing (3DP) filaments in North America through Asahi Kasei Plastics North America (APNA). The soft la Read more