Schedule a Call Back
Automation also enables companies to employ sustainable practices
 Interviews
Interviews- Nov 02,23

Related Stories

Birla Opus Paints inaugurates fourth plant; Targets Rs 100 billion in revenue
The Chamarajnagar plant will produce a range of products, including water-based paints, enamel paints, and wood finishes, catering specifically to the growing demand in southern India.
Read more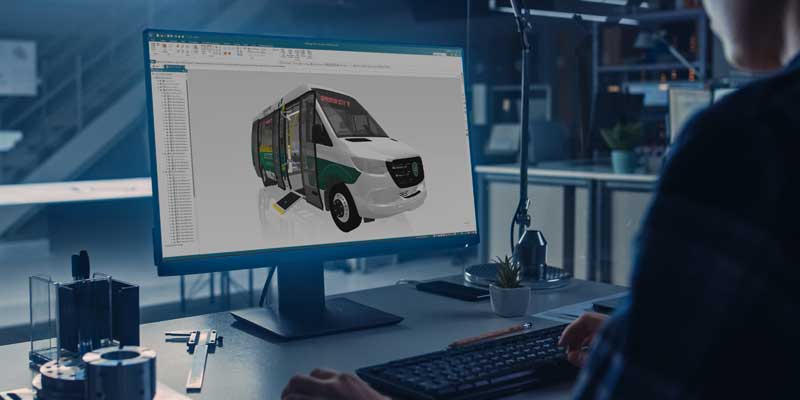
Siemens launches Solid Edge 2025 and Solid Edge X
Solid Edge 2025 is updated with improved data management and collaboration capabilities and enhancements across integrated mechanical and electrical design, simulation and machine tool programming.
Read more
Role of sustainable practices in manufacturing: Hitendra Bhargava
As the push for renewable energy and resource preservation deepens, sustainable practices in manufacturing arise as a leading light in nurturing a healthier planet.
Read more









