Schedule a Call Back
Women employed more than men in manufacturing jobs in urban India; MOSPI
 Industry News
Industry News- Aug 13,24

Related Stories
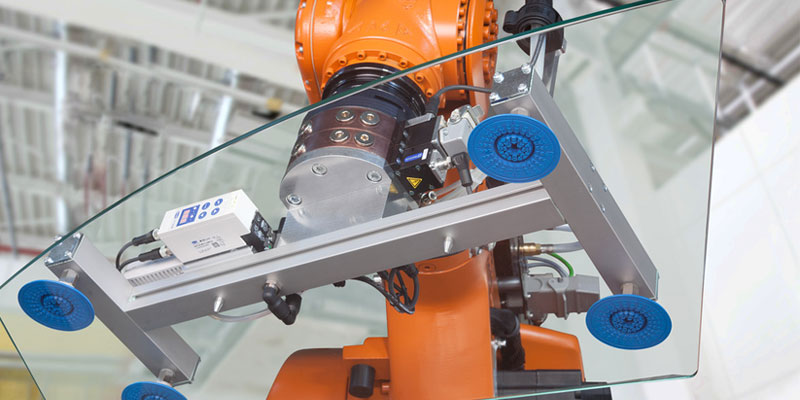
Air-Saving Vacuum Ejectors Cut Energy Use by Up to 90% in Automotive Plants
Air-saving vacuum ejectors are helping Indian automotive manufacturers reduce energy costs, cut carbon emissions and achieve rapid ROI while ensuring reliable, zero-defect production, shares Rajesh ..
Read more
India is at a pivotal ‘Make in India’ inflection point: Manoj Patil
In this interview, Manoj Patil, Promoter and Managing Director, Patil Automation Limited, outlines its growth journey, capacity expansion, acquisitions, design-led approach, market challenges, and t..
Read more
Salvagnini Italia Hosts Global Doors & Frames Industry Leadership Meet
Executives from 20+ countries met in Italy to discuss automation, flexibility and manufacturing complexity in doors and frames.
Read more













