Schedule a Call Back
How to leverage virtual and augmented reality in Industry 4.0?
 Articles
Articles- Nov 01,19
Related Stories

Avro India Launches Large-scale Flexible Plastic Recycling Facility in Ghaziabad
Avro India Limited has commissioned a greenfield recycling facility in Ghaziabad to process difficult-to-recycle flexible plastics, strengthening India’s circular economy and EPR compliance ecosys..
Read more
Garuda Aerospace Inaugurates Drone Battery Facility with DGCA Chief
Garuda Aerospace has inaugurated a drone battery manufacturing facility and a new academic block in Chennai, reinforcing its commitment to building a self-reliant and indigenous drone ecosystem in I..
Read more
India’s energy storage capacity set for 10-fold surge in 2026: IESA
India’s battery energy storage capacity is projected to rise nearly ten-fold in 2026 as projects move from tendering to execution, marking a pivotal year for the sector, according to IESA.
Read moreRelated Products
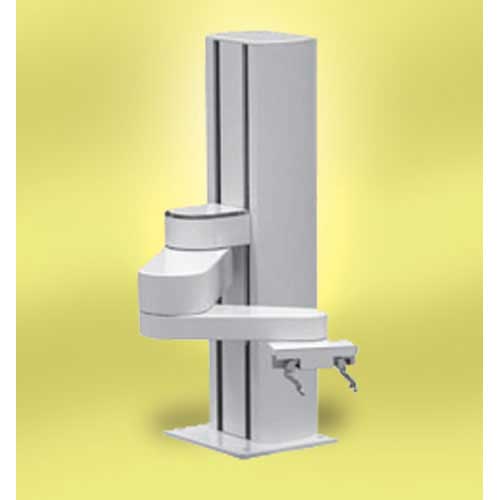

Collaborative Scara Robot
Malles Automated & Robotic Systems Private Limited
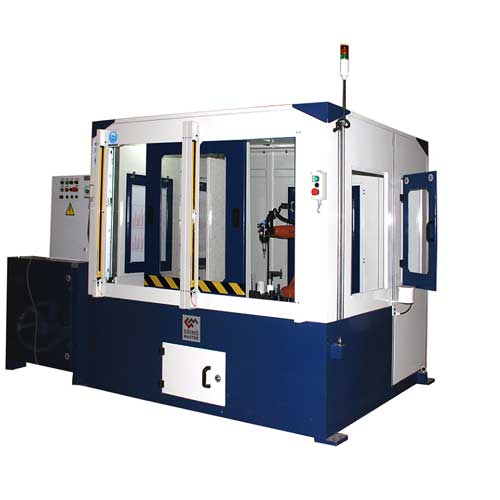

Robotic Deflashing of Aluminium Casting
Grind Master Robotic Deflashing Machine is an advanced and most reliable machine for Aluminium components. Robotic deflashing is a revolutionary technology developed by Grind Master Machines Pvt Lt Read more
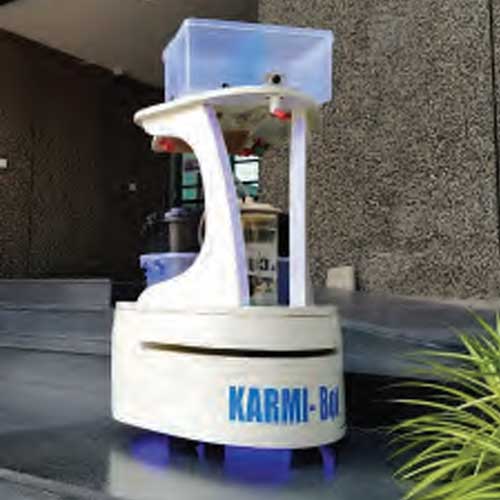

Karmi Bot
Asimov Robotics offers a wide range of Karmi Bot.













